D. Zone Of Maturation
A D B E С -F A Choose 00 B Choose pericycle phloem cortex xylem D epidermis endodermis Choose Choose Question. 4913BD although they occur along the medial cortex of the shaft also 130Loosers zones in the ribs and pelvis are rare.
The root region is arranged proximal to distal part in the following manner a Zone of cell elongation- Zone of cell maturation-Zone of cell division b Zone of cell division - Zone of cell elongation - Zone of cell maturation c Zone of cell maturation-Zone of cell elongation - Zone of cell division d Zone of cell maturation-Zone of cell division - Zone of cell elongation.
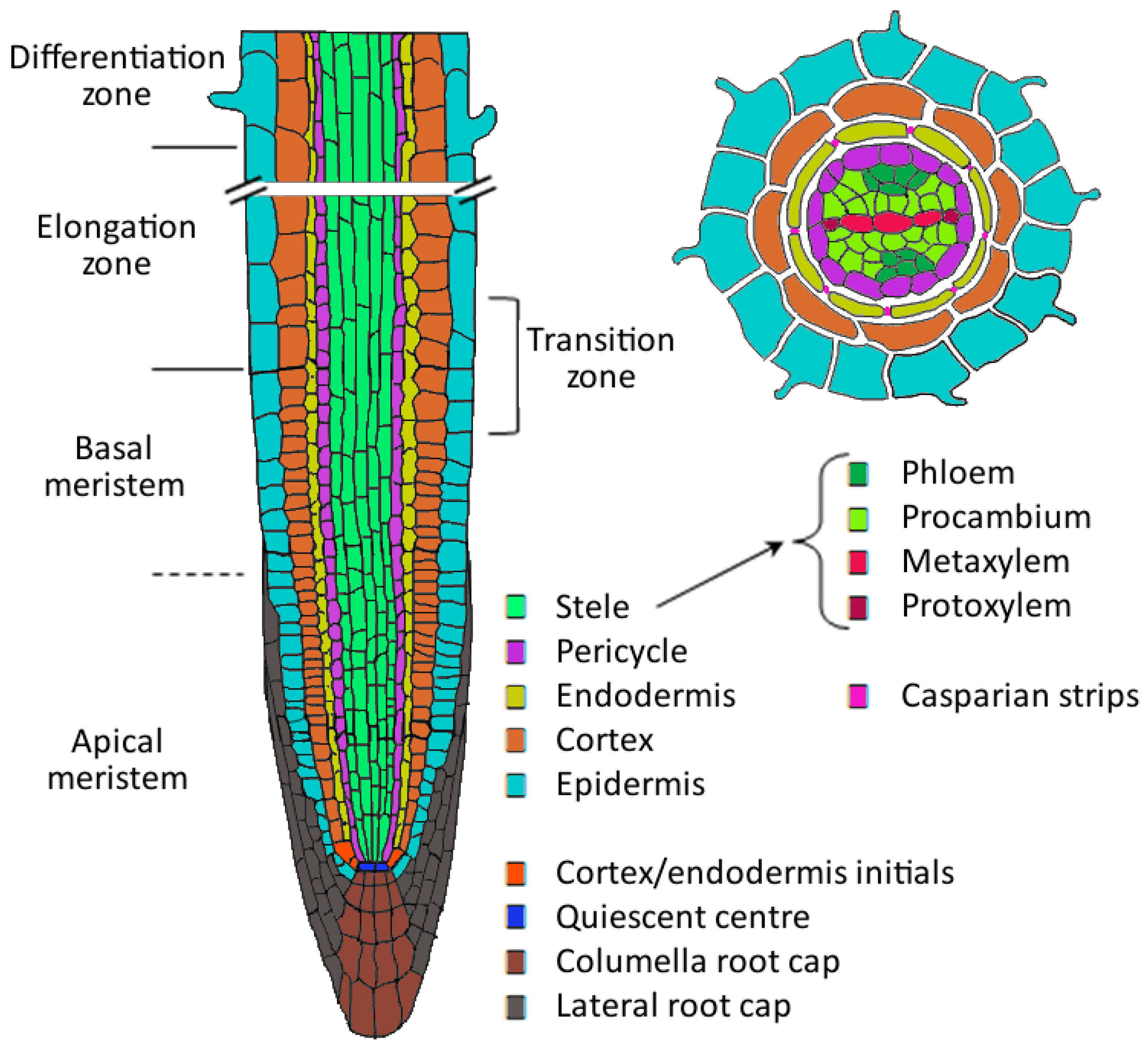
D. zone of maturation. Roots cap is at the tip. Iii Zone of elongation in which cells are newly formed cells which lose the power of division. Zone of cell division zone of elongation zone of maturation.
Root hair region is called the piliferous zone. Root slide showing root cap e. Chondrocytes in the next layer the zone of maturation and hypertrophy are older and larger than those in the proliferative zone.
A Photosynthesis b Allow gaseous exchange c Protection of apex d Provide mechanical support for stem 7 How does the root cap protect the apex of the root. A number of B cell subpopulations including B-1 B-2 and regulatory B cells have been identified. Before puberty chronological age correlates well with bone age but during adolescence bone age is more closely related to adult maturity levels so that bone age is related to the timing of puberty and growth in height in an individual Roche.
The answer is the option a C B E A D. 1How does a shoot apex differ from the apical meristem of a root with regards to the cap. This is followed by a zone of elongation and then root hair zone.
Followed by a zone of meristems. 2How would you explain this difference. Followed by a zone of meristems.
Zone of maturation zone of elongation zone of cell division. Zone of cell elongation In this zone cellular expansion is responsible for pushing the root cap and apical tip forward through the soil. These tend to occur in sites different from those in nutritional osteomalacia and are often present in the outer cortex of the bowed femur Fig.
Region of elongation where the newly-formed cells increase in length thereby lengthening the root. Since the identification of B cells in 1965 Cooper et al. A D B E С -F A Choose 00 B Choose pericycle.
Zone of elongation III. Zone of maturation The base of the root is defined as the maturation zone. Zone of maturation comes after all of them.
A number of B cell subpopulations including B-1 B-2 and regulatory B cells have been identified. Zone of cell division - This zone gives rise to the primary body of the. Why do you think root hairs occur only in the zone of maturation.
Cellular expansion in this zone is responsible for pushing the root cap and apical tip forward through the soil. Leaf slide of moncot or eudicot c. In this region functional cells are found.
1965 three has been tremendous progress in our understanding of B cell development maturation and function. Which of the following is a characteristic of the cells of the maturation zone. It makes new chondrocytes via mitosis to replace those that die at the diaphyseal end of the plate.
The question was asked in an online interview. Identify the labeled structures in the cross section of the zone of maturation of the dicot root model. A By secreting mucilage b By secreting amino acid c By secreting starch d By secreting antibody 8 Quiescent cells are active cells a True b False 9 The hypodermis is the outermost layer of cells of the cortex.
The zone of maturation comes at last. This intriguing question comes from Growth and Development in Plants topic in section Plant Growth and Development of Biology. Region of meristematic activity where apical meristem is present and increase the length of root.
A The epidermis of the root consists of a single layer of cells B The specialized root tissues can be seen at the zone of maturation C The pericycle is the outer layer of cells in the vascular cylinder and has the ability to form secondary or branch roots D The Casparian strip is a waxy lining on four sides of the cells of the endodermis that regulates the movement of materials. Iv Root hair zone which represents the zone of differentiation v Region or zone of mature cells forms the bulk of the root without undergoing any further change. 3Are all cells in the shoot apex the same size.
Zone of meristems have cells of very small size thin walled and with dense protoplasm. Since the identification of B cells in 1965 Cooper et al. The elongating cells complete their differentiation into the tissues of the primary body in this zone.
In cell maturation zone secondary growth takes place. B The specialized root tissues can be seen at the zone of maturation C The pericycle is the outer layer of cells in the vascular cylinder and has the ability to form secondary or branch roots D The Casparian strip is a waxy lining on four sides of the cells of the endodermis that regulates the movement of materials into and out of the vascular cylinder. 1965 three has been tremendous progress in our understanding of B cell development maturation and function.
The specialized root tissues can be seen at the zone of maturation The pericycle is the outer layer of cells in the vascular cylinder and has the ability to form secondary or branch roots The Casparian strip is a waxy lining on four sides of the cells of the endodermis that regulates the movement of materials into and out of the. Roots cap is at the tip. Monocot stem slide d.
This is followed by the zone of elongation and then the root hair zone. Eudicot woody stem slide b. Zone of cell division IV.
Identify the labeled structures in the cross section of the zone of maturation of the dicot root model. One or two large vacuoles occupy almost all of the cell volume in fully elongated cells. Bone maturation is the process whereby the tissue undergoes changes from the embryonic rudiment of bone to the adult form Roche 1986.
Region of maturation that bears unicellular root hairs which increases the surface area and helps in the absorption of water. Maturation zone contains the vascular cylinder and root hair. B-1 cells mainly originate from the fetal liver and contain B-1a and B-1b.
After skeletal maturation Loosers zones persist in patients with XLH. Zone of cell maturation V. Iii Zone of elongation in which cells are newly formed cells which lose the power of division.
Iv Root hair zone which represents the zone of differentiation v Region or zone of mature cells forms the bulk of the root without undergoing any further change. Zone of cell division zone of maturation zone of elongation. The following question is based on parts of a growing primary root.
The cells in zone of elongation undergo rapid elongation and enlargement and are responsible for the growth of the roots in length. Root slide showing zone of maturation. Root slide showing zone of maturation Feedback The correct answer is.
Zone of maturation zone of cell division zone of elongation. The proliferative zone is the next layer toward the diaphysis and contains stacks of slightly larger chondrocytes.

Regions Of Root From Base To Root Tip Are

Roots And Structure Chapter 7 Ppt Download

Ijms Free Full Text Gene Networks Involved In Hormonal Control Of Root Development In Arabidopsis Thaliana A Framework For Studying Its Disturbance By Metal Stress Html

Bio 172 Ch 28 Plant Structure And Growth Flashcards Quizlet
0 Response to "D. Zone Of Maturation"
Post a Comment